A series of earthquakes struck southern Tibet on January 7, near the Nepal border. Its epicentre was about 75 kilometres northeast of Mount Everest and close to Nepal, but no major damage was reported there. This quake was the most powerful in the area since the catastrophic earthquake in April 2015 in Nepal, which resulted in approximately 10,000 fatalities.
What exactly is an earthquake? Which countries are the most earthquake-prone? Why is the Himalayan region seismically active? Here’s what you need to know.
Earthquakes
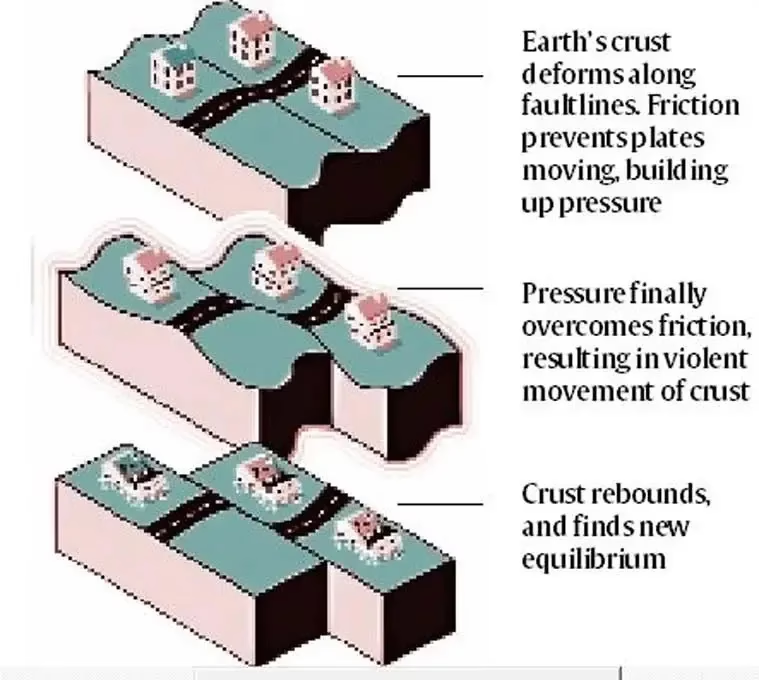
An earthquake is an intense shaking of the ground caused by movement under the earth’s surface. It happens when two blocks of the earth suddenly slip past one another, according to USGS. This releases stored-up ‘elastic strain’ energy in the form of seismic waves, which spreads through the earth and cause the shaking of the ground.
The earth’s outermost surface, crust, is fragmented into tectonic plates. The edges of the plates are called plate boundaries, which are made up of faults. The tectonic plates constantly move at a slow pace, sliding past one another and bumping into each other. As the edges of the plates are quite rough, they get stuck with one another while the rest of the plate keeps moving. Earthquake occurs when the plate has moved far enough and the edges unstick on one of the faults.
The location below the earth’s surface where the earthquake starts is called the hypocenter, and the location directly above it on the surface of the earth is called the epicentre.
Why is the Himalayan zone seismically active?
1. The Himalayan mountain range began to form approximately 40 to 50 million years ago when the Eurasian and Indian tectonic plates started to collide. According to the USGS, “Seismicity in the Himalaya dominantly results from the continental collision of the India and Eurasia plates, which are converging at a relative rate of 40-50 mm/yr.”
2. At least five earthquakes of magnitude greater than 7 have struck the Hindu Kush region since 1950. “This region has a peculiar tectonic formation. While the Indian plate is getting under the Himalayas, a phenomenon that is occurring all along the Himalayan range, the Eurasian plate is getting subducted under the Pamir mountains. In addition, there are several other faultlines. This is the convergence point for several seismic forces.”
Can earthquakes be predicted?
No. An accurate prediction of an earthquake requires some sort of a precursory signal from within the earth that indicates a big quake is on the way. Moreover, the signal must occur only before large earthquakes so that it doesn’t indicate every small movement within the earth’s surface. Currently, there is no equipment to find such precursors, even if they exist.
Most Earthquake-Prone Countries in the World
1. Several Asian countries are highly prone to earthquakes, with China and Indonesia experiencing the most seismic activity. Japan records the highest number of earthquakes globally when considering the relative frequency.
2. Indonesia stands out as the most earthquake-prone country, having experienced 2,212 earthquake events with a magnitude of 4 or above. This figure places Indonesia above both Mexico and the Philippines, according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS).
3. In an analysis of the most devastating earthquakes globally, China surpasses Indonesia, as reported by the U.S. government’s National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The NOAA’s data sheds light on the impact of seismic activity across the globe, highlighting the countries most affected by these catastrophic events over the nearly three-decade period.
India’s Vulnerability to Earthquakes
Ranking as the seventh most earthquake-prone country in the world, India has endured 58 significant earthquakes throughout its history and is vulnerable to seismic activity. India’s vulnerability to earthquakes stems from its geographical position at the convergence of multiple tectonic plates, its intricate geological structure, and a rapidly growing population paired with widespread unregulated construction practices. According to ndma.gov.in, approximately 59 per cent of its land area is at risk of experiencing moderate to severe seismic events, capable of registering an intensity of VII on the MSK scale or higher.
The Theory Of Plate Tectonics
The surface of the Earth is divided into 7 major plates and several minor ones. They move a few centimetres a year, riding on semi-molten layers of rock underneath the crust. As the plates move, they pull apart or collide, unleashing the powerful movements known as earthquakes.
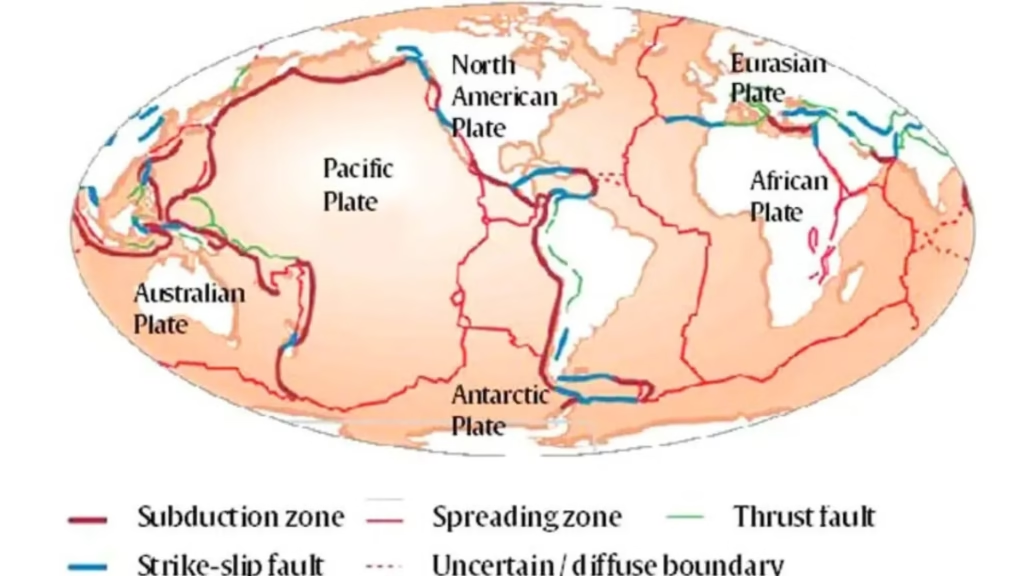
Types of Plate Boundary
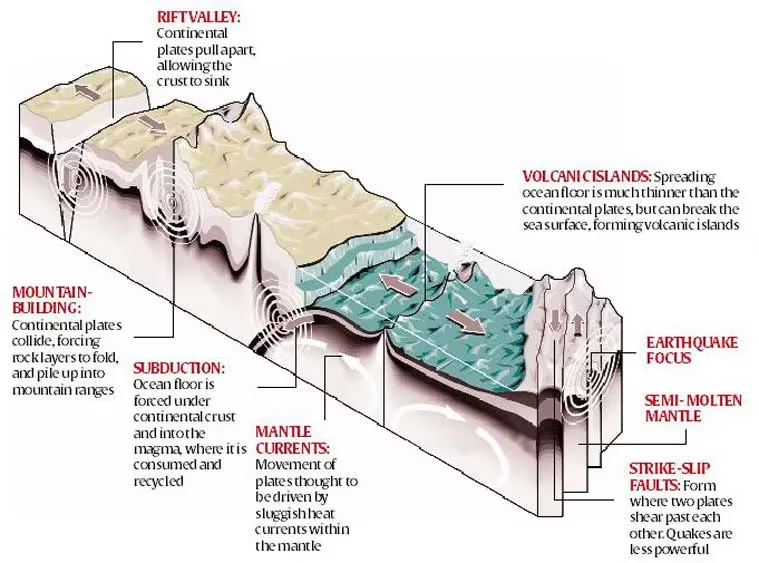
Slippage Along A Fault
Earthquake Wave Types
1. When an earthquake occurs, it generates seismic waves that cause the shaking we experience. There are two major types of seismic waves: body waves and surface waves. Body waves comprise P and S waves, and they are called body waves because they can travel through the Earth’s interior, rather than being confined near the surface.
2. Primary or ‘P’ wave is a type of sound wave that travels through rock. In a P wave, the rock particles are alternately compressed and expanded, a process known as compressions and dilatations. This is why P waves are also referred to as compressional waves. They are capable of traveling through solids, liquids, and gases. Notably, P waves can move through the liquid outer core of the Earth.
3. In Secondary or ‘S’ wave, the rock particles slide past one another, which creates shear – hence, S waves are also known as shear waves. S waves cannot travel through liquids or gases, which means they do not propagate through the ocean or the outer core.
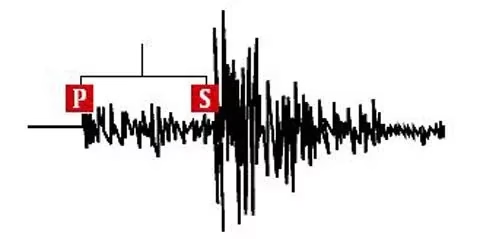
Surface waves are named for their tendency to be confined near the Earth’s surface, as opposed to traveling through the Earth’s interior like P and S waves. There are two main types of surface waves: Love waves, which are shear waves that are trapped near the surface, and Rayleigh waves, which exhibit particle motions similar to those of water particles in ocean waves.